Rain Gardens
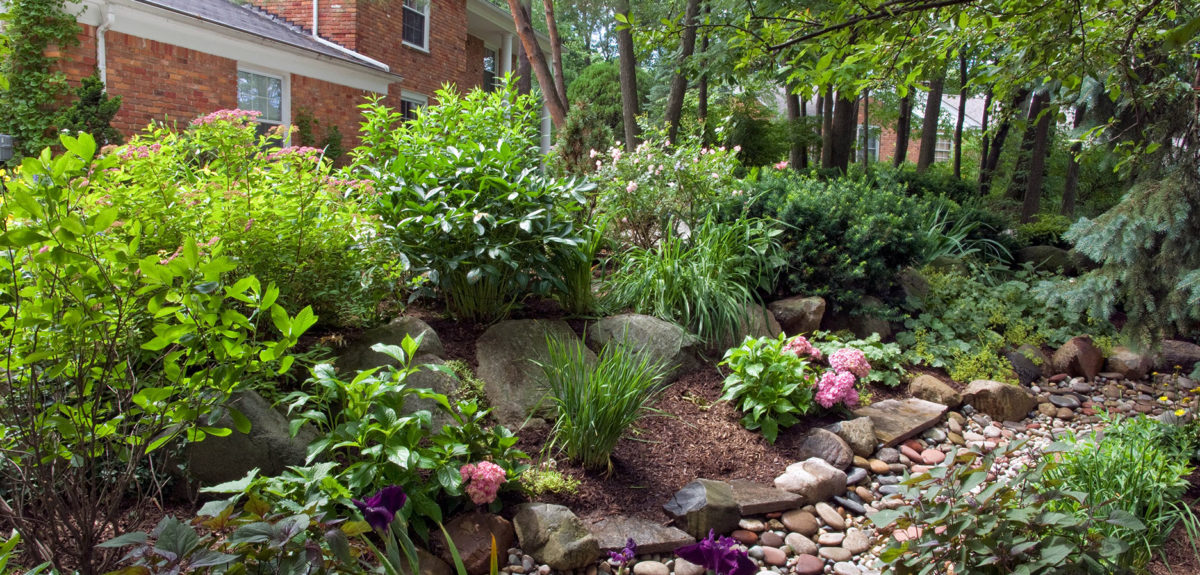

What is a rain garden?
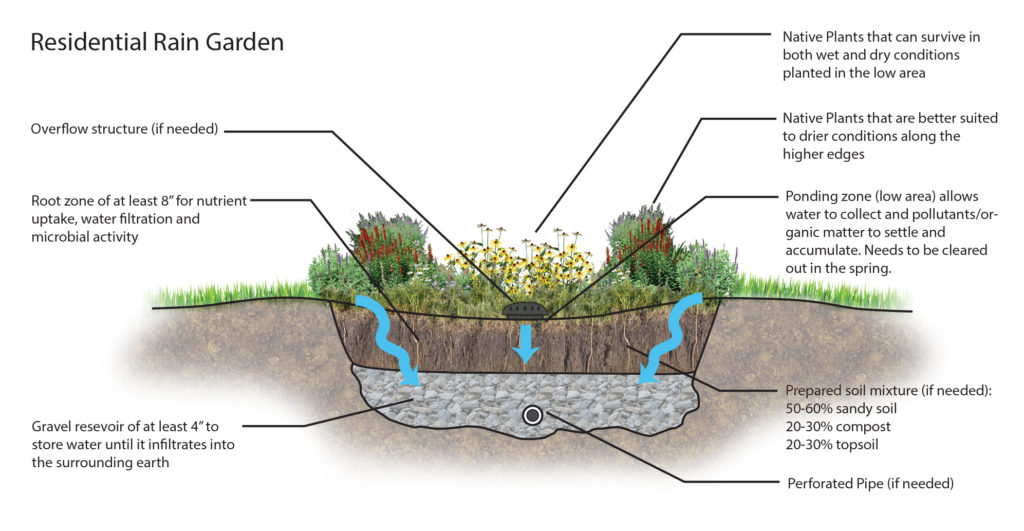
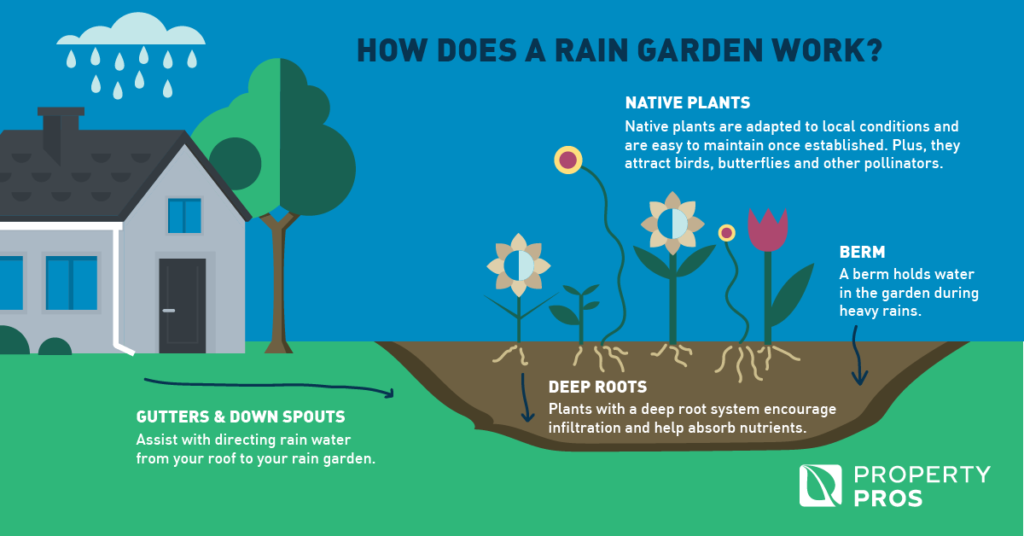
A rain garden is a depressed area in the landscape that collects water from roof downspouts, asphalt, or sump pump discharge and allows it to soak into the ground rather than enter the storm sewer system. Less runoff from your house means a lower amount of channel erosion and fewer hanging solids and pollution in the waterways.
Why should I plant a rain garden?
When you have native plants, your rain garden will not require pesticides or fertilizer causing them to be cost effective, low maintenance, and offer a beautiful way to reduce and filter runoff from your property. Rain gardens also provide a butterfly habitat, aid in preventing floods, and make your lawn more attractive.
How do rain gardens work?
Every time it rains, water runs off impermeable surfaces, like rooftops and driveways, gathering pollutants such as particles of dirt, fertilizer, chemicals, oil, trash, and bacteria. The rain garden allows the water to be filtered by vegetation and funnel into the soil recharging groundwater aquifers. Overall, rain gardens are effective in removing up to 90% of nutrients and chemicals and up to 80% of sediments from rainwater runoff. In comparison to a conventional lawn, rain gardens allow for 30% more water to soak into the ground. They will drain within 12-48 hours and help prevent the breeding of mosquitoes, as well.
How big should a rain garden be?
It should have an area about 20% the size of the roof, patio, or pavement area draining into it. If you live in a residential home or small building, your rain garden should be between 100 and 400 square feet. Regardless of size, each rain garden can make a big impact. Typically, rain gardens are shaped longer than they are wide and positioned perpendicular to the slope of the land in order to catch the maximum amount of rainfall. They should also be placed at least 10 feet from building foundations and not near water ponds for an extended period of time.
Let us know if we can help you plant a rain garden on your property!



